The field of healthcare has been revolutionized by advances in medical technology that continue to improve the quality of patient care. Among the many innovations in this domain are multipara monitors and medical ventilator machines. Both are critical pieces of equipment that play a significant role in monitoring and supporting critically ill patients. These devices are often used together in intensive care units (ICUs), operating rooms, and emergency settings to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. If you have ever wondered what a multipara monitor is and how it works in conjunction with a medical ventilator machine, this article will provide an in-depth explanation.
What Is a Multipara Monitor?
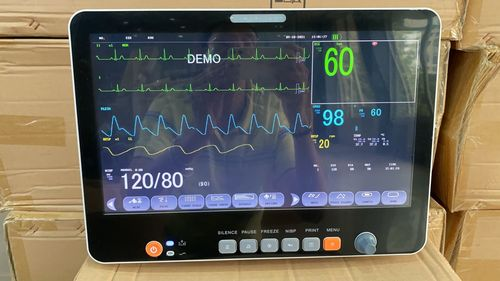
A multipara monitor, also known as a multi-parameter monitor, is a sophisticated medical device designed to track and display multiple vital parameters simultaneously. It acts as the “eyes and ears” of healthcare providers, offering real-time insight into a patient’s physiological status. The purpose of a multipara monitor is to collect, process, and display data so that clinicians can identify potential health risks and take appropriate measures.
Commonly monitored parameters include:
- Heart Rate and ECG: Tracks the electrical activity of the heart to identify arrhythmias or other cardiac problems.
- Blood Pressure (BP): Both invasive and non-invasive methods can be employed to monitor a patient’s blood pressure.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): Measures the level of oxygen in the patient’s blood via a pulse oximeter.
- Respiratory Rate (RR): Monitors the number of breaths a patient takes per minute.
- Temperature: Tracks body temperature, which can indicate infection or other systemic conditions.
- End-Tidal CO2 (ETCO2): Measures the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled by a patient, providing insight into respiratory efficiency.
What Is a Medical Ventilator Machine?
A medical ventilator machine, often simply referred to as a ventilator, is a life-saving device that provides respiratory support to patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own. This inability to breathe efficiently can arise due to various reasons, such as lung diseases (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pneumonia), neurological conditions, or injury.
The ventilator takes over or assists the process of breathing by delivering oxygen-rich air into the lungs and removing carbon dioxide.
The Two Main Types of Ventilators
- Invasive Ventilators: Require artificial airways such as endotracheal tubes or tracheostomy tubes to deliver respiratory support.
- Non-invasive Ventilators (NIV): Use masks or other external interfaces to support breathing.
Key Settings on a Ventilator
- Tidal Volume: The amount of air delivered to the lungs with each breath.
- Respiratory Rate (RR): The number of breaths initiated by the ventilator per minute.
- Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP): Keeps the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs) open during exhalation to improve oxygenation.
- Fraction of Inspired Oxygen (FiO2): The concentration of oxygen delivered to the patient.
How Do a Multipara Monitor and a Medical Ventilator Machine Work Together?
The integration between a multipara monitor and a medical ventilator machine is essential for providing comprehensive care to critically ill patients. Each device serves a complementary role—while the ventilator provides life-sustaining respiratory support, the multipara monitor continuously tracks and displays the patient’s vital signs to assess their overall condition.
Key Ways They Work Together
1. Monitoring Respiratory Parameters
When a patient is on a medical ventilator machine, one of the most critical functions of the multipara monitor is to keep track of respiratory parameters such as respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and end-tidal CO2. This data is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the mechanical ventilation.
2. Detecting Hemodynamic Changes
A multipara monitor also tracks cardiac functions like heart rate and blood pressure, which can be affected by ventilator interactions.
3. Alarm Systems for Immediate Action
Both devices are equipped with advanced alarm systems. However, when used together, the multipara monitor acts as a central hub for alarms from both the ventilator and its own data stream.
4. Continuous Data Integration
Modern ICU setups often feature integrated systems where a multipara monitor and a medical ventilator machine can communicate through advanced interfaces.
5. Customizable Settings for Patient Needs
Both devices can be personalized to suit the specific needs of a patient. The multipara monitor reflects these changes in real time, providing instant feedback.
6. Trend Analysis and Documentation
Multipara monitors can store and display trends over hours, days, or longer. These trends are invaluable for monitoring the progress of ventilated patients.
The Importance of Using a Multipara Monitor with a Medical Ventilator Machine
Using a multipara monitor alongside a ventilator is not just convenient—it is critical. Together, they provide a more complete picture of a patient’s condition.
- Early Detection of Complications
- Optimal Ventilator Management
- Reduced Risk of Adverse Events
- Better Patient Outcomes
Challenges of Integration
Despite their numerous benefits, integrating a multipara monitor with a medical ventilator machine is not without challenges.
- Complexity of Equipment
- Data Overload
- Cost
Future of Multipara Monitors and Medical Ventilator Machines
Technological advances are addressing many of these challenges:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Remote Monitoring
- Compact, Portable Devices
Conclusion
A multipara monitor and a medical ventilator machine are indispensable tools in critical care medicine. When used together, they provide comprehensive monitoring and support, ensuring that patients receive life-saving treatments while minimizing risks.
In the face of rising healthcare needs, understanding the interplay between these two machines helps underscore their critical roles in modern medicine. Their integration forms the cornerstone of successful patient management in intensive care settings, improving survival rates and paving the way for even more sophisticated healthcare solutions in the future. Ultimately, mastering these technologies not only enhances the care provided to patients but also empowers healthcare providers to work more effectively in high-stakes environments.